Indication Aimovig® is indicated for the preventive treatment of migraine in adults.
Indication Aimovig® is indicated for the preventive treatment of migraine in adults.
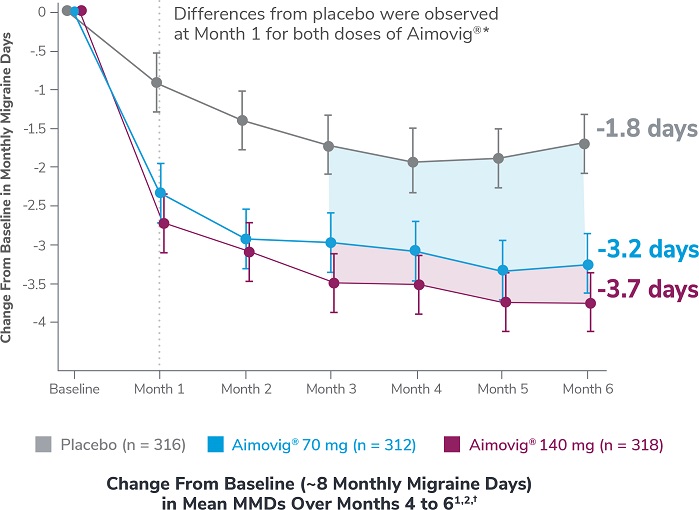
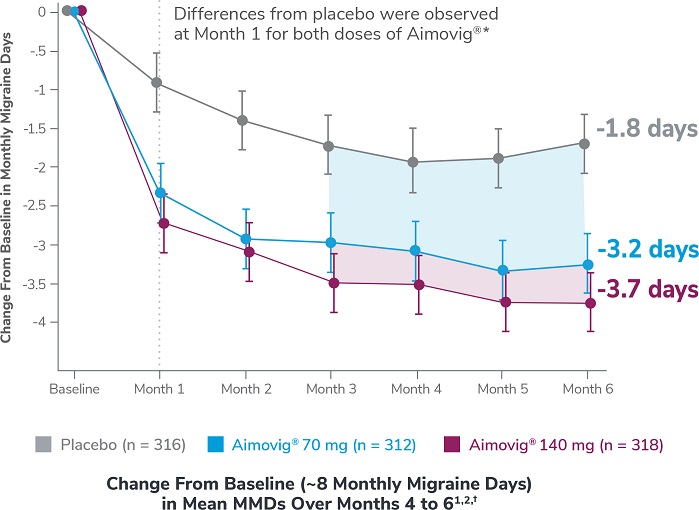
This was a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of adult episodic migraine patients.1,2
Aimovig® was evaluated for the prevention of episodic migraine in patients aged 18 to 65 years with 4 to 14 monthly migraine days (MMDs) in this multicenter, 24-week study.1
*Earliest post-baseline prespecified assessment.2
†Least-square means are presented. For Aimovig® 70 mg, the difference from placebo was -1.4 (95% CI: -1.9, -0.9). For Aimovig® 140 mg, the difference from placebo was -1.9 (95% CI: -2.3, -1.4).1,2
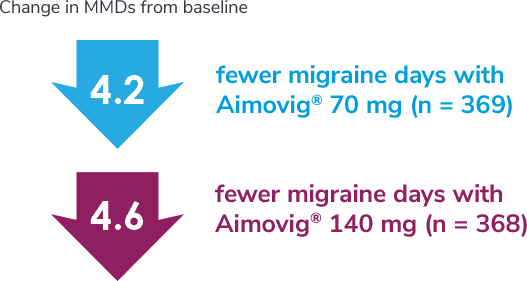
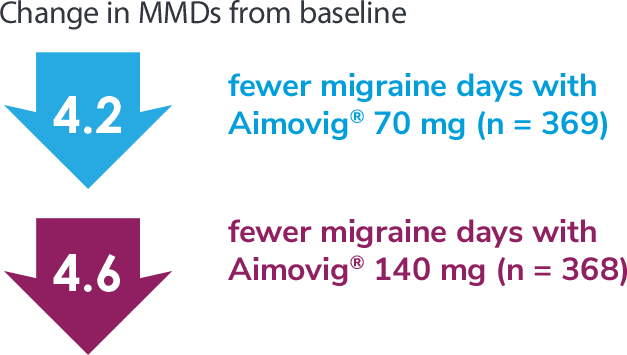
Following the 24-week DBTP, patients were re-randomized to receive Aimovig® 70 mg (n = 421) or 140 mg (n = 424) during the ATP, with re-randomization stratified by treatment groups assigned during the DBTP.3
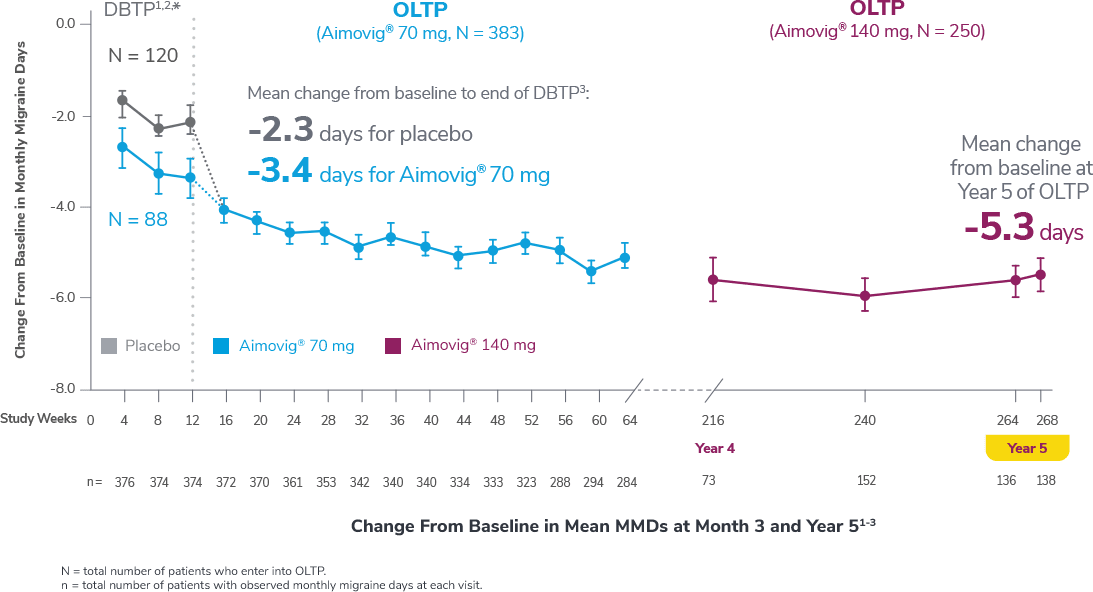
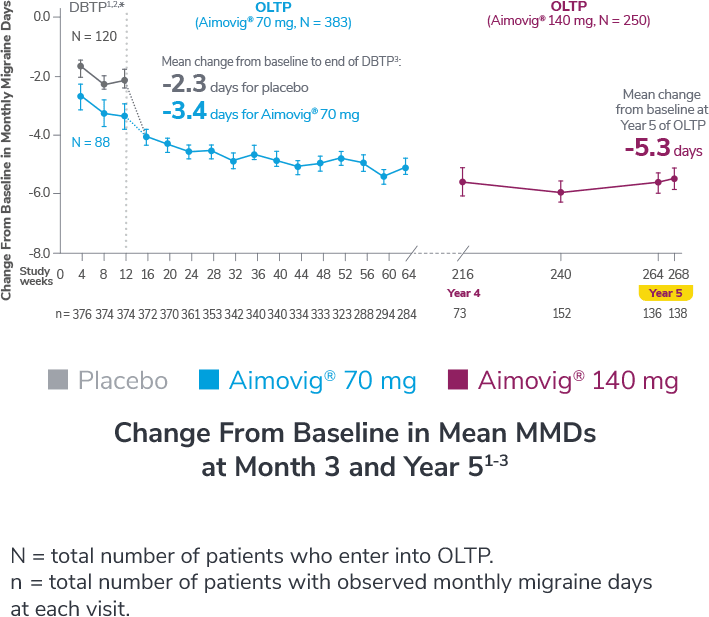
Consider open-label treatment phase study limitations when interpreting results. The OLTP was not blinded, not controlled, and included inherent self-selection bias for remaining in the trial. Overall, a total of 167 patients (43.6%) discontinued during the study, of which 18 patients (4.7%) discontinued due to adverse events.1
*Study included additional dosage arms, which were not included in the FDA-approved labeling.3
*Study included additional dosage arms, which were not included in the FDA-approved labeling.3
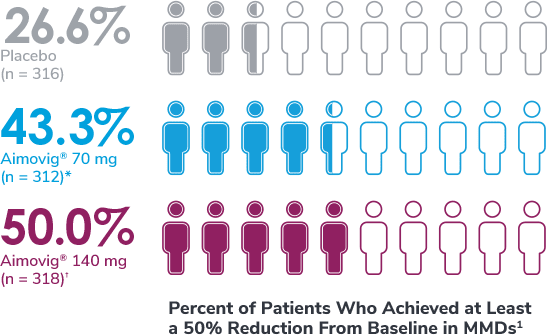
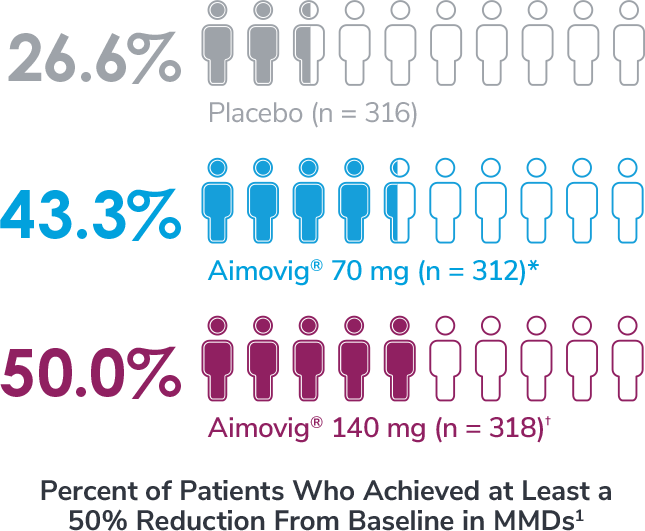
*Odds of achieving a ≥50% reduction were significantly higher (2.1x, 95% CI: 1.5, 3.0) for the Aimovig® 70 mg group than for the placebo group (P<0.001).1,2
†Odds of achieving a ≥50% reduction were significantly higher (2.8x, 95% CI: 2.0, 3.9) for the Aimovig® 140 mg group than for the placebo group (P<0.001).1,2

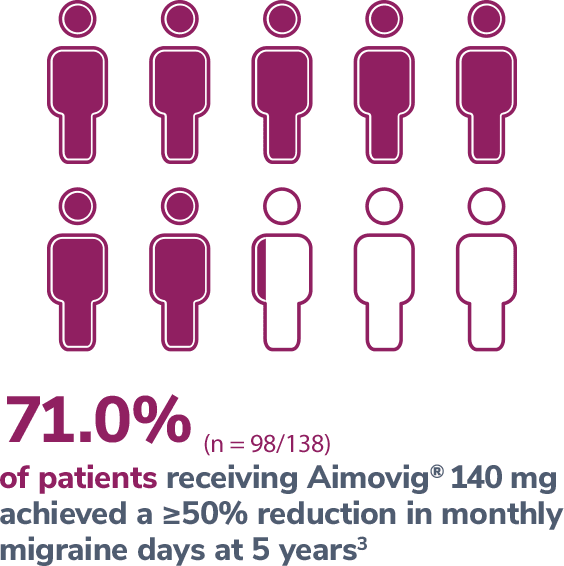
Consider open-label treatment phase study limitations when interpreting results. The OLTP was not blinded, not controlled, and included inherent self-selection bias for remaining in the trial. Overall, a total of 167 patients (43.6%) discontinued during the study, of which 18 patients (4.7%) discontinued due to adverse events.5
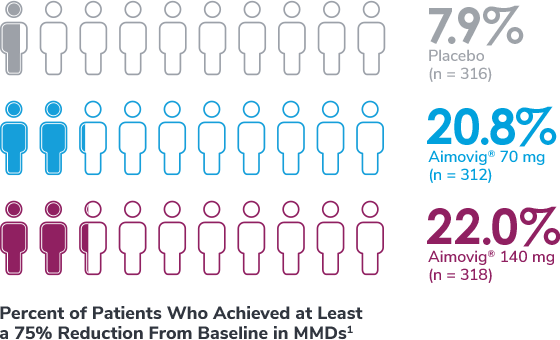
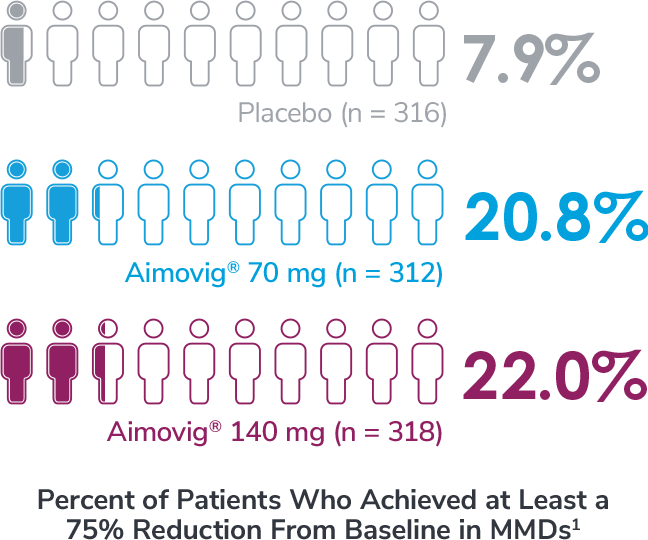


Consider open-label treatment phase study limitations when interpreting results. The OLTP was not blinded, not controlled, and included inherent self-selection bias for remaining in the trial. Overall, a total of 167 patients (43.6%) discontinued during the study, of which 18 patients (4.7%) discontinued due to adverse events.5
*Represents only patients who entered into open-label treatment phase.4
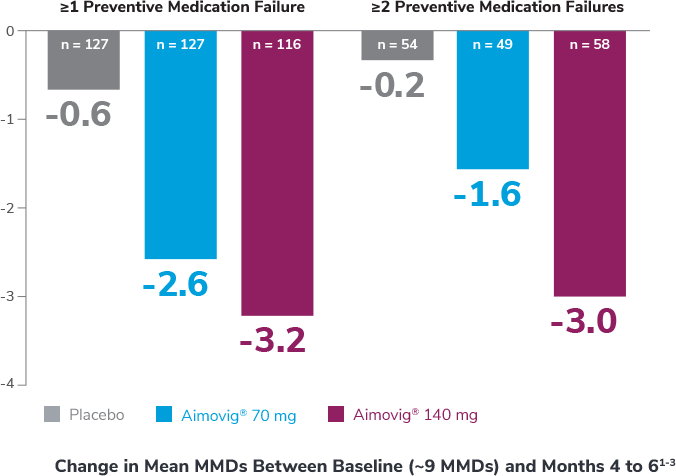
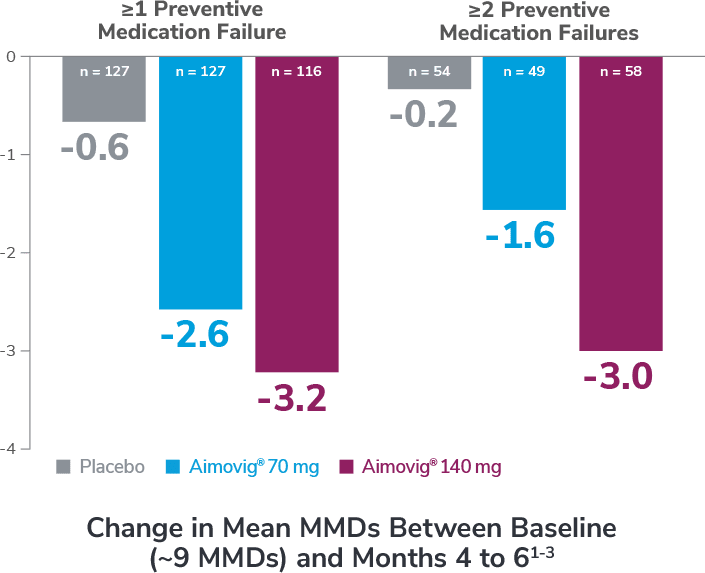
Subgroup analysis is exploratory and has not been adjusted for multiple comparisons. No conclusions of statistical or clinical significance can be drawn.
Preventive medications had failed due to lack of efficacy or intolerance by self-report.1
In the overall study population
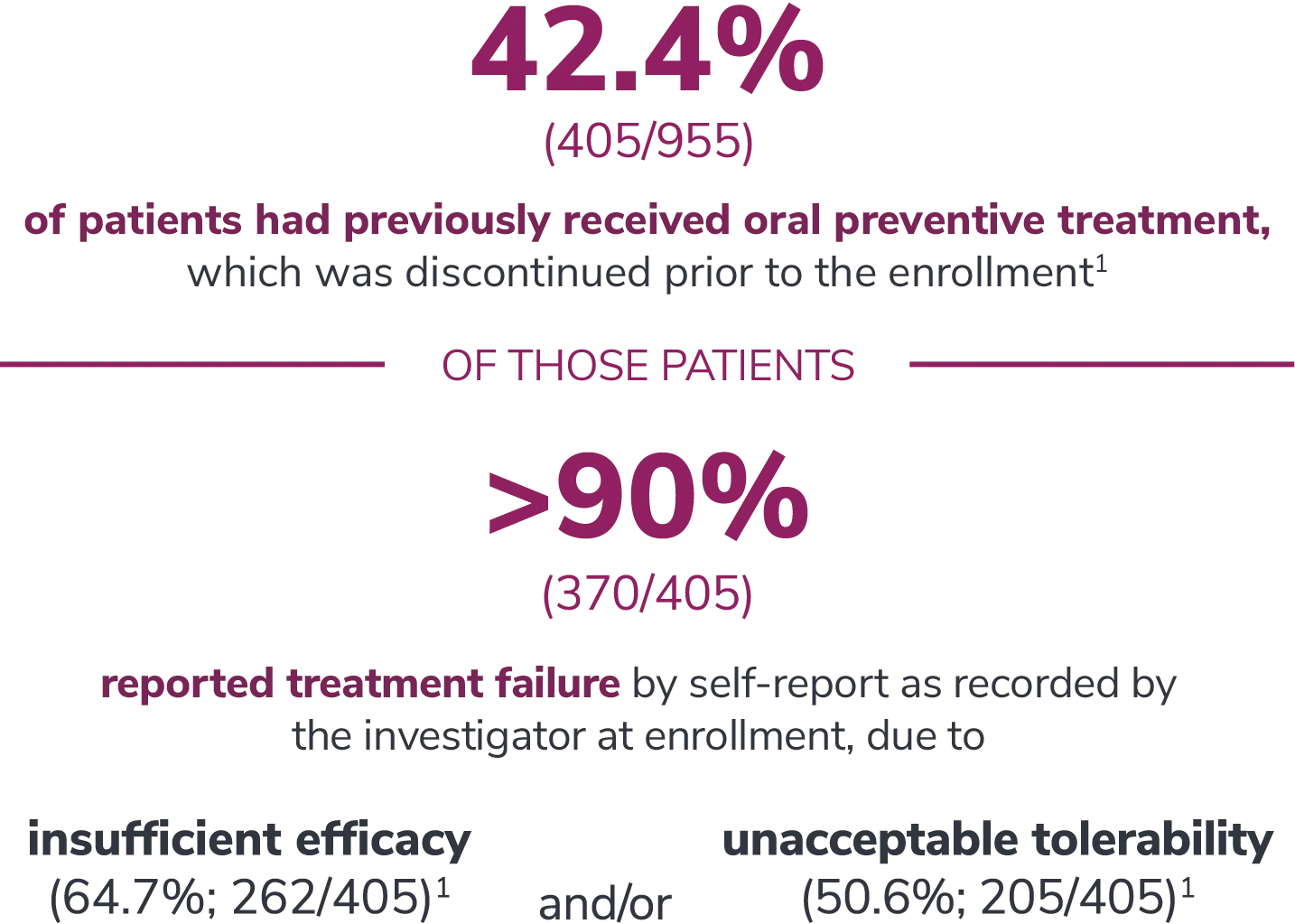
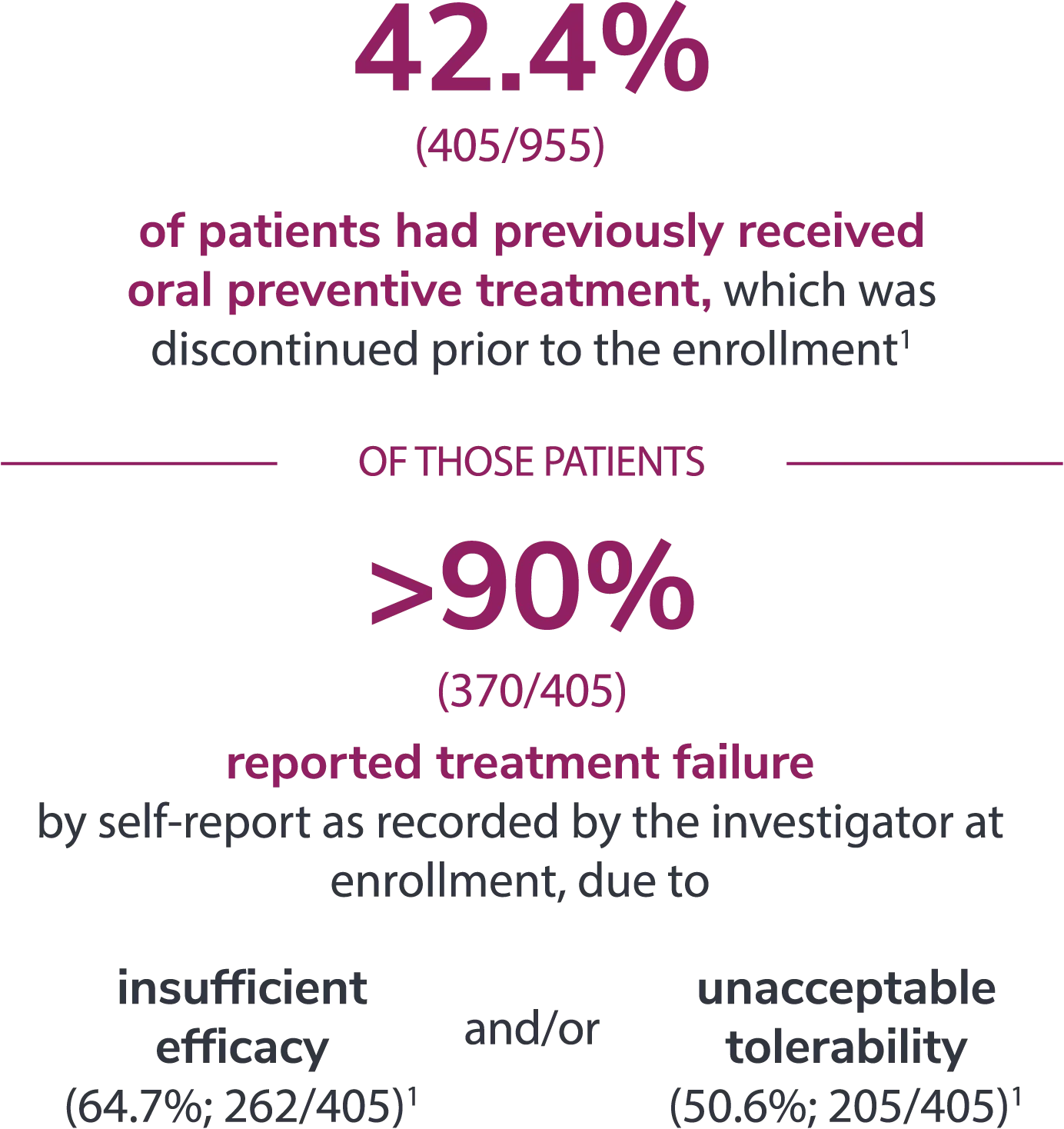
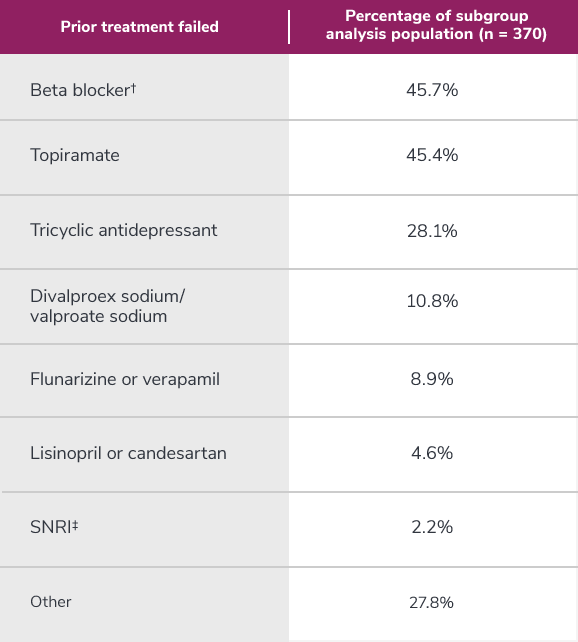
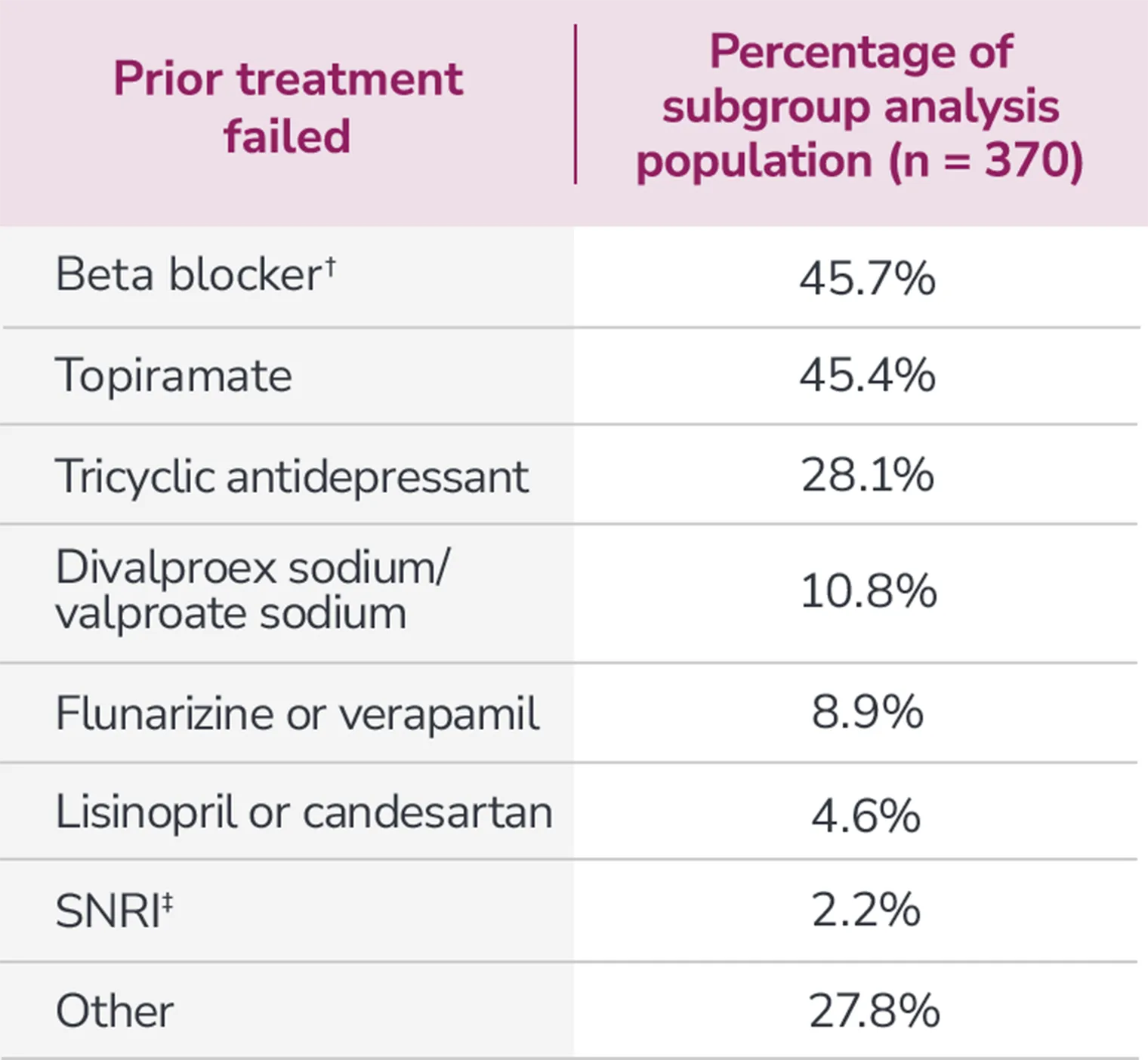
*Categories are not mutually exclusive and patients may contribute to more than one category.
†Atenolol, bisoprolol, metoprolol, nadolol, nebivolol, pindolol, propranolol, and timolol.
‡Venlafaxine, desvenlafaxine, duloxetine, and milnacipran.
Aimovig® (erenumab-aooe) is indicated for the preventive treatment of migraine in adults.
Contraindication: Aimovig® is contraindicated in patients with serious hypersensitivity to erenumab-aooe or to any of the excipients. Reactions have included anaphylaxis and angioedema.
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Hypersensitivity reactions, including rash, angioedema, and anaphylaxis, have been reported with Aimovig® in post marketing experience. Most reactions were not serious and occurred within hours of administration, although some occurred more than one week after administration. If a serious or severe reaction occurs, discontinue Aimovig® and initiate appropriate therapy.
Constipation with Serious Complications: Constipation with serious complications has been reported following the use of Aimovig® in the postmarketing setting. There were cases that required hospitalization, including cases where surgery was necessary. The onset of constipation was reported after the first dose in a majority of these cases, but patients also reported later on in treatment. Aimovig® was discontinued in most reported cases. Constipation was one of the most common (up to 3%) adverse reactions reported in clinical studies.
Monitor patients treated with Aimovig® for severe constipation and manage as clinically appropriate. Concurrent use of medications associated with decreased gastrointestinal motility may increase the risk for more severe constipation and the potential for constipation-related complications.
Hypertension: Development of hypertension and worsening of pre-existing hypertension have been reported following the use of Aimovig® in the postmarketing setting. Many of the patients had pre-existing hypertension or risk factors for hypertension. There were cases requiring pharmacological treatment and, in some cases, hospitalization. Hypertension may occur at any time during treatment but was most frequently reported within seven days of dose administration. In the majority of the cases, the onset or worsening of hypertension was reported after the first dose. Aimovig® was discontinued in many of the reported cases.
Monitor patients treated with Aimovig® for new-onset hypertension, or worsening of pre-existing hypertension, and consider whether discontinuation of Aimovig® is warranted if evaluation fails to establish an alternative etiology.
Adverse Reactions: The most common adverse reactions in clinical studies (≥ 3% of Aimovig®-treated patients and more often than placebo) were injection site reactions and constipation.
Please see Aimovig® full Prescribing Information.
Contraindication: Aimovig® is contraindicated in patients with serious hypersensitivity to erenumab-aooe or to any of the excipients. Reactions have included anaphylaxis and angioedema.
Hypersensitivity reactions: Hypersensitivity reactions, including rash, angioedema, and anaphylaxis, have been reported with Aimovig® in post marketing experience. Most reactions were not serious and occurred within hours of administration, although some occurred more than one week after administration. If a serious or severe
References: 1. Aimovig® (erenumab-aooe) Prescribing Information. Thousand Oaks, CA: Amgen Inc; 2021. 2. Goadsby PJ, Reuter U, Hallström Y, et al. A controlled trial of erenumab for episodic migraine. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(22):2123-2132. 3. Goadsby PJ, Reuter U, Hallström Y, et al. One-year sustained efficacy of erenumab for episodic migraine: Results of the STRIVE study. Neurology. 2020;95:e469-e479. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000010019. 4. Data on file, Amgen; 2024.
References: 1. Ashina M, Goadsby PJ, Reuter U, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of erenumab in migraine prevention: Results from a 5-year, open-label treatment phase of a randomized clinical trial. Eur J Neurol. 2021;28:1716-1725. doi:10.1111/ene.14175. 2. Data on file, Amgen; [Ph 2 EM CSR T14-1.1, January 28, 2016]. 3. Sun H, Dodick DW, Silberstein S, et al. Safety and efficacy of AMG 334 for prevention of episodic migraine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(4):382-390. 4. Data on file, Amgen; 2024.
References: 1. Aimovig® (erenumab-aooe) Prescribing Information. Thousand Oaks, CA: Amgen Inc; 2021. 2. Goadsby PJ, Reuter U, Hallström Y, et al. A controlled trial of erenumab for episodic migraine. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(22):2123-2132. 3. Data on file, Amgen; [Ph 2 EM CSR, November 25, 2020]. 4. Sun H, Dodick DW, Silberstein S, et al. Safety and efficacy of AMG 334 for prevention of episodic migraine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(4):382-390. 5. Ashina M, Goadsby PJ, Reuter U, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of erenumab in migraine prevention: Results from a 5-year, open-label treatment phase of a randomized clinical trial. Eur J Neurol. 2021;28:1716-1725. doi:10.1111/ene.14175. 6. Data on file, Amgen; 2024.
References: 1. Bröessner G, Reuter U, Bonner J, et al. Achievement of ≥75% and 100% response in patients treated with erenumab: 24-week results from the STRIVE study. Poster presented at: 18th Congress of the International Headache Society; September 7-10, 2017; Vancouver, Canada. 2. Data on file, Amgen; [Ph 2 EM CSR, November 25, 2020]. 3. Sun H, Dodick DW, Silberstein S, et al. Safety and efficacy of AMG 334 for prevention of episodic migraine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(4):382-390. 4. Data on file, Amgen; [Ph 2 EM CSR T14-4.3.19, January 28, 2016]. 5. Ashina M, Goadsby PJ, Reuter U, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of erenumab in migraine prevention: Results from a 5-year, open-label treatment phase of a randomized clinical trial. Eur J Neurol. 2021;28:1716-1725. doi:10.1111/ene.14715. 6. Data on file, Amgen; 2024.
References: 1. Goadsby PJ, Paemeleire K, Bröessner G, et al. Efficacy and safety of erenumab (AMG 334) in episodic migraine patients with prior preventive treatment failure: a subgroup analysis of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Cephalalgia. 2019. doi:10.1177/0333102419835459. 2. Goadsby PJ, Paemeleire K, Bröessner G, et al. Efficacy of erenumab in subjects with episodic migraine with prior preventive treatment failure(s). Presented at: 18th Congress of the International Headache Society; September 7-10, 2017; Vancouver, Canada. 3. Data on file, Amgen; [Ph 3 EM CSR Table 10-3, February 20, 2017]. 4. Data on file, Amgen; 2024.
References: 1. Goadsby PJ, Paemeleire K, Bröessner G, et al. Efficacy and safety of erenumab (AMG 334) in episodic migraine patients with prior preventive treatment failure: a subgroup analysis of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Cephalalgia. 2019. doi:10.1177/0333102419835459. 2. Data on file, Amgen; 2024.